What is Tree and Use off it. (English / hindi )
What is Tree and Use off it.
In plant science, a tree is a perpetual plant with a lengthened stem, or trunk, supporting branches and leaves in most species. In some utilizations, the meaning of a tree might be smaller, incorporating just woody plants with optional development, plants that are usable as timber or plants above a predefined tallness. In more extensive definitions, the taller palms, tree plants, bananas, and bamboos are additionally trees. Trees are not a scientific classification but rather incorporate an assortment of plant species that have freely developed a trunk and branches as an approach to tower above different plants to go after daylight. Trees will in general be seemingly perpetual, some arriving at a few thousand years of age. Trees have been in presence for 370 million years. It is evaluated that there are a little more than 3 trillion develop trees in the world.
A tree commonly has many auxiliary branches bolstered clear of the ground by the trunk. This trunk ordinarily contains woody tissue for quality, and vascular tissue to convey materials starting with one piece of the tree then onto the next. For most trees it is encompassed by a layer of bark which fills in as a defensive hindrance. Underneath the ground, the roots branch and spread out broadly; they serve to grapple the tree and concentrate dampness and supplements from the dirt. Above ground, the branches separate into littler branches and shoots. The shoots commonly bear leaves, which catch light vitality and convert it into sugars by photosynthesis, giving the nourishment to the tree's development and improvement.
Trees as a rule replicate utilizing seeds. Blooms and natural product might be available, yet some trees, for example, conifers, rather have dust cones and seed cones. Palms, bananas, and bamboos likewise produce seeds, yet tree plants produce spores.
Trees assume a critical job in decreasing disintegration and directing the atmosphere. They expel carbon dioxide from the climate and store huge amounts of carbon in their tissues. Trees and timberlands give a living space to many species of creatures and plants. Tropical rainforests are among the most biodiverse territories on the planet. Trees give shade and safe house, timber for development, fuel for cooking and warming, and natural product for nourishment just as having many different employments. In parts of the world, woods are contracting as trees are cleared to expand the measure of land accessible for agribusiness. Due to their life span and convenience, trees have consistently been respected, with consecrated forests in different societies, and they assume a job in many of the world's legends.
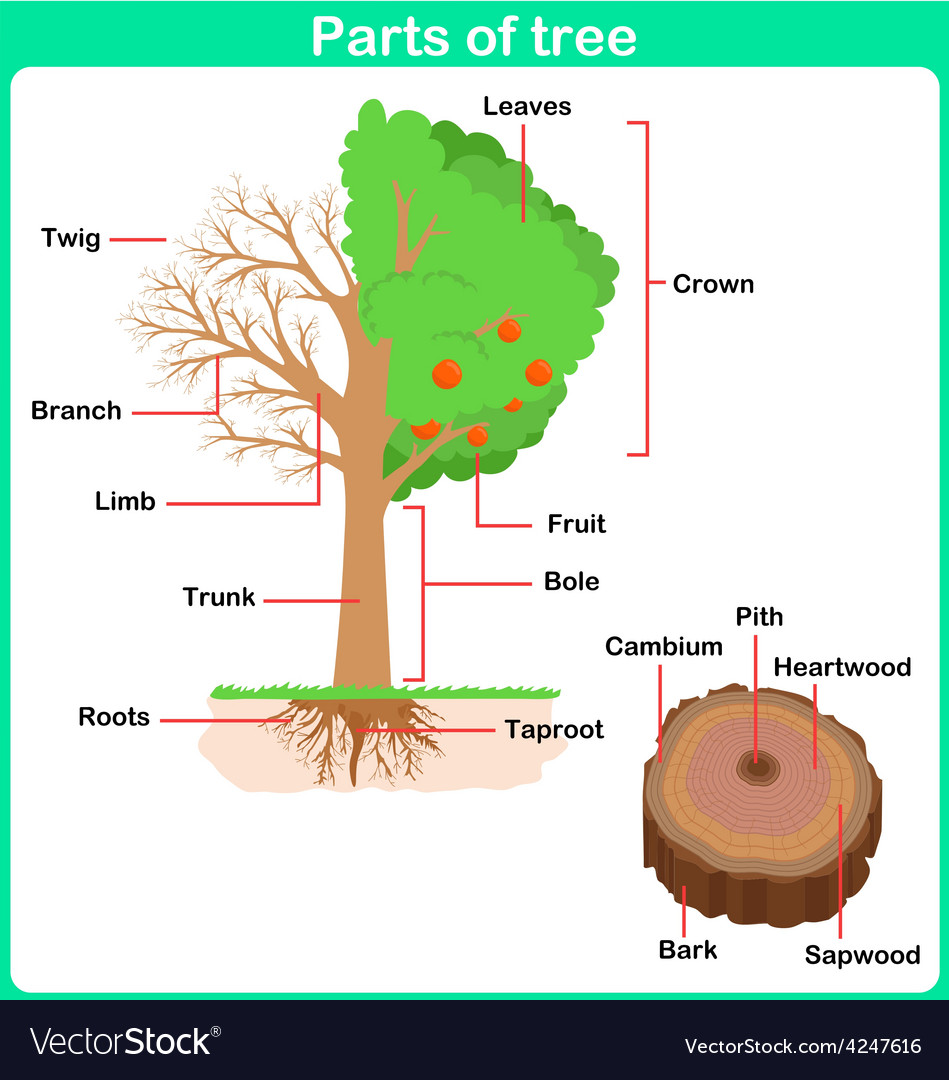
"Parts of Trees"
Trees have three primary parts - the leaves, the trunk and the roots. The upper piece of the tree with the branches is known as the crown.
Needles or leaves are the piece of the tree that make sugar from air and water. They do this by a synthetic procedure called photosynthesis in which vitality from the sun, carbon dioxide from the air, and water recombine to frame sugars and oxygen.
Stomates are modest gaps that control the measure of air that enters and leaves the tree.
Chlorophyll is a compound that makes leaves green. It is found inside the plant's cells where chloroplasts retain the sun's vitality for photosynthesis.

The trunk has a few layers.
The external bark shields the tree from fire or creepy crawlies and protects it from extraordinary warmth and cold.
The phloem is the layer of cells that structures a pipeline to convey sugars from the leaves to the remainder of the tree. As these cells bite the dust, they become some portion of the external bark.
The cambium is the developing piece of the trunk. Every year the cambium creates new phloem and sapwood. These phones develop all the more gradually in the winter and this more slow development delivers the tree's yearly rings. These yearly rings can assist us with finding the age of a tree. The most established piece of the tree is consistently within.
The sapwood is the pipeline that conveys water and supplements from the roots up to the leaves. As new layers build up, the internal layers kick the bucket and become heartwood.

Heartwood is dead wood in the focal point of the tree. It invigorates the tree its.
Roots have two occupations - to stay the tree to the earth and to assimilate water and supplements from the dirt.
Trees have parasites that live in and on the root cells and assist them with retaining water and supplements. Consequently, the parasites acquire nourishment from the tree.
पादप विज्ञान में, एक पेड़ एक लम्बे तने, या ट्रंक के साथ एक स्थायी पौधा है, ज्यादातर प्रजातियों में शाखाओं और पत्तियों का समर्थन करता है। कुछ उपयोगों में, एक पेड़ का अर्थ छोटा हो सकता है, जिसमें वैकल्पिक विकास के साथ सिर्फ लकड़ी के पौधे शामिल होते हैं, ऐसे पौधे जो लकड़ी के रूप में उपयोग किए जाते हैं या पूर्वनिर्धारित लम्बाई से ऊपर के पौधे होते हैं। अधिक व्यापक परिभाषाओं में, लम्बी हथेलियाँ, पेड़ पौधे, केले और बाँस इसके अतिरिक्त पेड़ हैं। पेड़ एक वैज्ञानिक वर्गीकरण नहीं हैं, बल्कि पौधों की प्रजातियों के वर्गीकरण को शामिल करते हैं, जिन्होंने दिन के उजाले के बाद जाने के लिए अलग-अलग पौधों के ऊपर टॉवर के दृष्टिकोण के रूप में एक ट्रंक और शाखाएं विकसित की हैं। पेड़ सामान्य रूप से सदा के लिए लगेंगे, कुछ का आगमन कुछ हज़ार साल की उम्र में होगा। पेड़ 370 मिलियन वर्षों से मौजूद हैं। यह मूल्यांकन किया जाता है कि दुनिया में 3 ट्रिलियन से अधिक विकसित पेड़ हैं।
एक पेड़ में आमतौर पर कई सहायक शाखाएं होती हैं, जो ट्रंक द्वारा जमीन से साफ होती हैं। इस ट्रंक में आम तौर पर गुणवत्ता के लिए वुडी टिशू होते हैं, और संवहनी ऊतक को सामग्री को पेड़ के एक टुकड़े से शुरू करने के लिए फिर अगले पर होता है। अधिकांश पेड़ों के लिए इसे छाल की एक परत द्वारा घेर लिया जाता है जो रक्षात्मक बाधा के रूप में भर जाती है। जमीन के नीचे, जड़ें शाखा और मोटे तौर पर फैल जाती हैं; वे पेड़ को चराते हैं और गंदगी से नमी और पूरक पदार्थों को केंद्रित करते हैं। जमीन के ऊपर, शाखाएं लिटलर शाखाओं और शूट में अलग हो जाती हैं। अंकुर आमतौर पर पत्तियों को सहन करते हैं, जो प्रकाश जीवन शक्ति को पकड़ते हैं और इसे प्रकाश संश्लेषण द्वारा शर्करा में परिवर्तित करते हैं, जिससे पेड़ के विकास और सुधार को पोषण मिलता है।
वृक्ष विघटन को कम करने और वातावरण को निर्देशित करने में एक महत्वपूर्ण कार्य मानते हैं। वे जलवायु से कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड को बाहर निकालते हैं और बड़ी मात्रा में कार्बन को अपने ऊतकों में जमा करते हैं। पेड़ और इमारती लकड़ी जीवों और पौधों की कई प्रजातियों को रहने की जगह देते हैं। उष्णकटिबंधीय वर्षावन ग्रह पर सबसे अधिक जैव विविधता वाले प्रदेश हैं। पेड़ छाया और सुरक्षित घर, विकास के लिए लकड़ी, खाना पकाने और वार्मिंग के लिए ईंधन, और कई अलग-अलग रोजगार के रूप में पोषण के लिए प्राकृतिक उत्पाद देते हैं। दुनिया के कुछ हिस्सों में, जंगल अनुबंधित कर रहे हैं क्योंकि कृषि व्यवसाय के लिए सुलभ भूमि की माप का विस्तार करने के लिए पेड़ों को साफ किया जाता है। उनके जीवन काल और सुविधा के कारण, पेड़ों का लगातार सम्मान किया गया है, विभिन्न समाजों में संरक्षित जंगलों के साथ, और वे दुनिया के कई किंवदंतियों में नौकरी करते हैं।
एक नियम के रूप में पेड़ बीजों के उपयोग को दोहराते हैं। खिलने और प्राकृतिक उत्पाद उपलब्ध हो सकते हैं, फिर भी कुछ पेड़, उदाहरण के लिए, कॉनिफ़र, बल्कि धूल के शंकु और बीज शंकु हैं। हथेलियों, केले और बांस इसी तरह बीज पैदा करते हैं, फिर भी पेड़ पौधे बीजाणु पैदा करते हैं।
Stomates मामूली अंतराल होते हैं जो हवा की माप को नियंत्रित करते हैं जो पेड़ में प्रवेश करता है और छोड़ देता है।
सुई या पत्ते पेड़ का टुकड़ा है जो हवा और पानी से चीनी बनाते हैं। वे प्रकाश संश्लेषण नामक एक सिंथेटिक प्रक्रिया द्वारा करते हैं जिसमें सूर्य से जीवन शक्ति, हवा से कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड, और पानी के पुनर्संयोजन से शर्करा और ऑक्सीजन को फ्रेम करना होता है।
(Trunk )ट्रंक में कुछ परतें हैं।
क्लोरोफिल एक यौगिक है जो पत्तियों को हरा बनाता है। यह पौधे की कोशिकाओं के अंदर पाया जाता है जहां क्लोरोप्लास्ट प्रकाश संश्लेषण के लिए सूर्य की जीवन शक्ति को बनाए रखता है।
बाहरी छाल पेड़ को आग या खौफनाक क्रॉल से बचाती है और इसे असाधारण गर्मी और ठंड से बचाती है।
फ्लोएम कोशिकाओं की परत है जो पत्तियों से शक्कर को पेड़ के शेष हिस्से तक पहुंचाने के लिए एक पाइपलाइन की संरचना करता है। जैसे ही ये कोशिकाएं धूल को काटती हैं, वे बाहरी छाल का कुछ हिस्सा बन जाते हैं।
कैम्बियम ट्रंक का विकासशील टुकड़ा है। हर साल कैम्बियम नए फ्लोएम और सैपवुड बनाता है। ये फोन सर्दियों में धीरे-धीरे सभी विकसित करते हैं और यह अधिक धीमी गति से विकास पेड़ के वार्षिक छल्ले को बचाता है। ये वार्षिक वलय वृक्ष की आयु ज्ञात करने में हमारी सहायता कर सकते हैं। पेड़ का सबसे स्थापित टुकड़ा लगातार भीतर है।
सॅपवुड वह पाइपलाइन है जो पानी तक पहुँचती है और जड़ों से पत्तियों तक पहुँचती है। जैसे-जैसे नई परतें बनती हैं, आंतरिक परतें बाल्टी को लात मारती हैं और हार्टवुड बन जाती हैं।
हार्टवुड पेड़ के केंद्र बिंदु में मृत लकड़ी है। यह पेड़ को मजबूत बनाता है।
पेड़ों में परजीवी होते हैं जो जड़ कोशिकाओं में रहते हैं और पानी और पूरक आहार को बनाए रखने में उनकी सहायता करते हैं। नतीजतन, परजीवी पेड़ से पोषण प्राप्त करते हैं।
Comments